
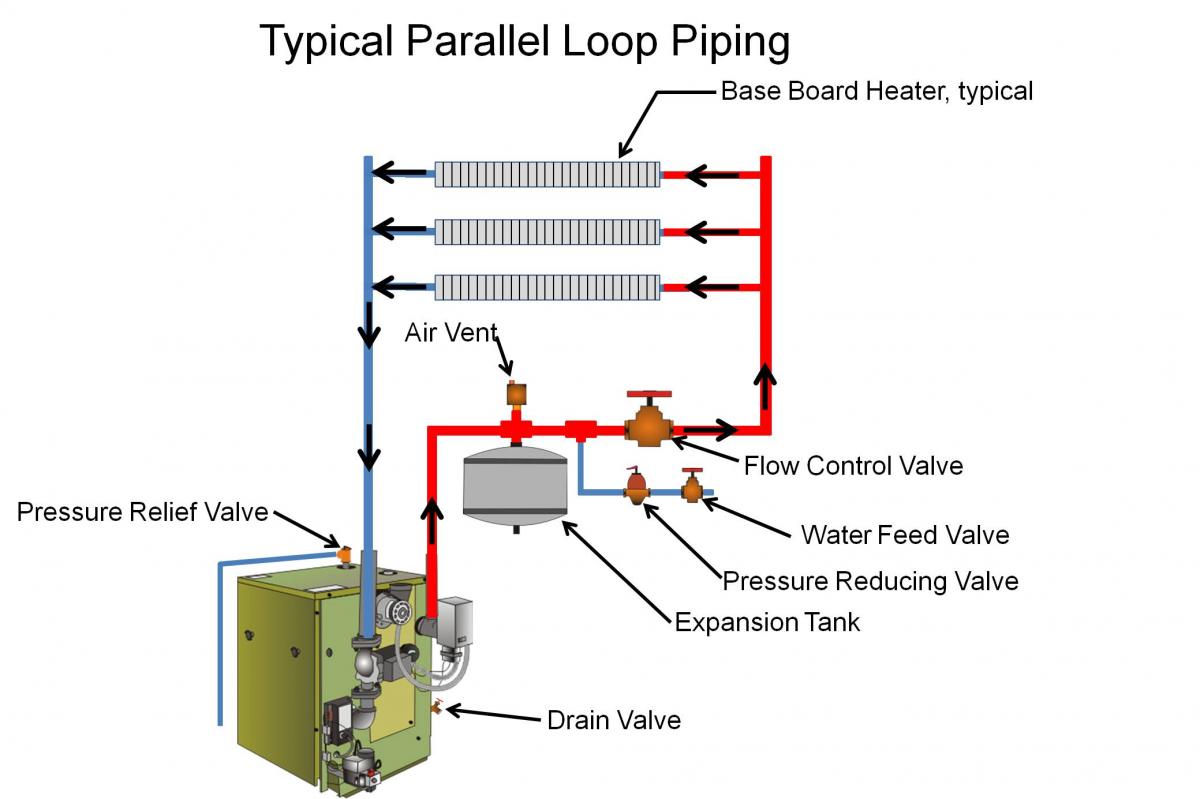
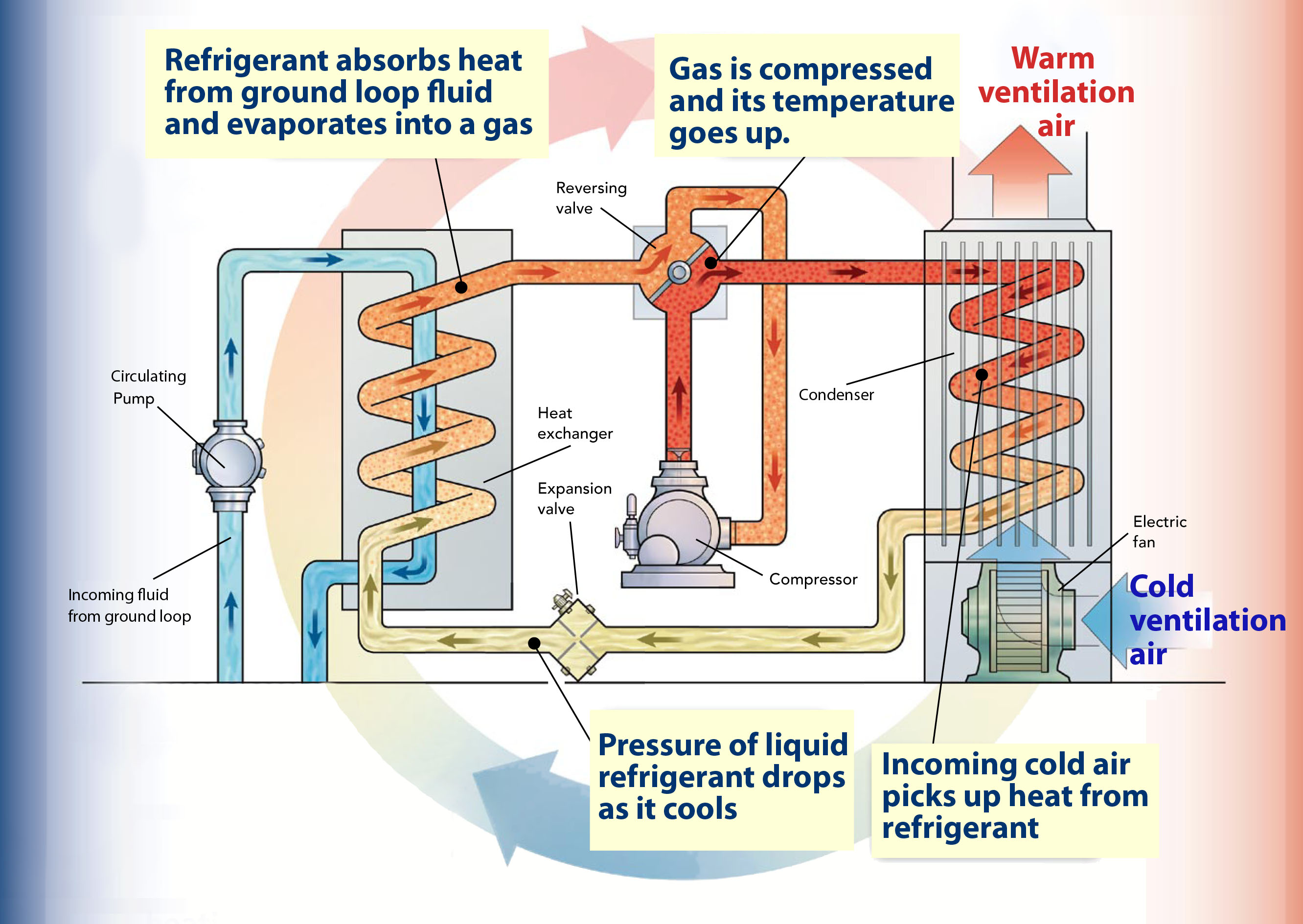
There are many various kinds of baffles, and the choice of baffle form, spacing, and geometry depends on the allowable flow rate of the drop in shell-side force, the need for tube support, and the flow-induced vibrations. One of the fluids flows through the tube side and the other fluid flows outside the tubes, but inside the shell (shell side).īaffles are used to support the tubes, direct the fluid flow to the tubes in an approximately natural manner, and maximize the turbulence of the shell fluid. In a shell-and-tube heat exchanger, two fluids at different temperatures flow through the heat exchanger. Where it can reduce thermal stress and produce more uniform rate of heat transfer. While the counter flow heat exchanger has more significant advantages compared to parallel flow design. Where two fluids are expected to be taken to exactly the same temperature, the parallel flow configuration is beneficial. Which indicates that the partnership is a distinct disadvantage if it is intended a design is to increase the cold fluid temperature. Owing to the large temperature differential arising from the high thermal voltage, the temperature profiles of the two heat exchangers display two significant disadvantages in the parallel-flow design. If this is done under comparable conditions, more heat is transferred to the counter-flow device than to the parallel flow heat exchanger. The figure above illustrates the parallel and counter-flow flow directions of the fluid exchanger. (c) Counter flow, where at opposite ends, hot and cold fluids join, flow in the opposite direction and exit at opposite ends. (b) Parallel flow, where at the same point, the hot and cold liquids join, flow in the same direction and exit at the same end. The flow may be a current flow or parallel flow in a double pipe heat exchanger. (a) When the other fluid flows into the annular gap between two tubes, one fluid flows through the smaller pipe. However, since double pipe heat exchangers are simple, they are used to teach heat exchanger design basics to students as the fundamental rules for all heat exchangers are the same. On the other hand, their low efficiency coupled with the high space occupied in large scales, has led modern industries to use more efficient heat exchangers like shell and tube or plate.

On one hand, these heat exchangers are cheap for both design and maintenance, making them a good choice for small industries. Sometimes direct knowledge of the LMTD is not available and the NTU method is used.ĭouble pipe heat exchangers are the simplest exchangers used in industries. In most simple systems this is the " log mean temperature difference" (LMTD). The driving temperature across the heat transfer surface varies with position, but an appropriate mean temperature can be defined. The exchanger's performance can also be affected by the addition of fins or corrugations in one or both directions, which increase surface area and may channel fluid flow or induce turbulence. 3: Shell and tube heat exchanger, 2-pass shell side, 2-pass tube side (2-2 countercurrent)įor efficiency, heat exchangers are designed to maximize the surface area of the wall between the two fluids, while minimizing resistance to fluid flow through the exchanger. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. Partial view into inlet plenum of shell and tube heat exchanger of a refrigerant based chiller for providing air-conditioning to a buildingĪ heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
